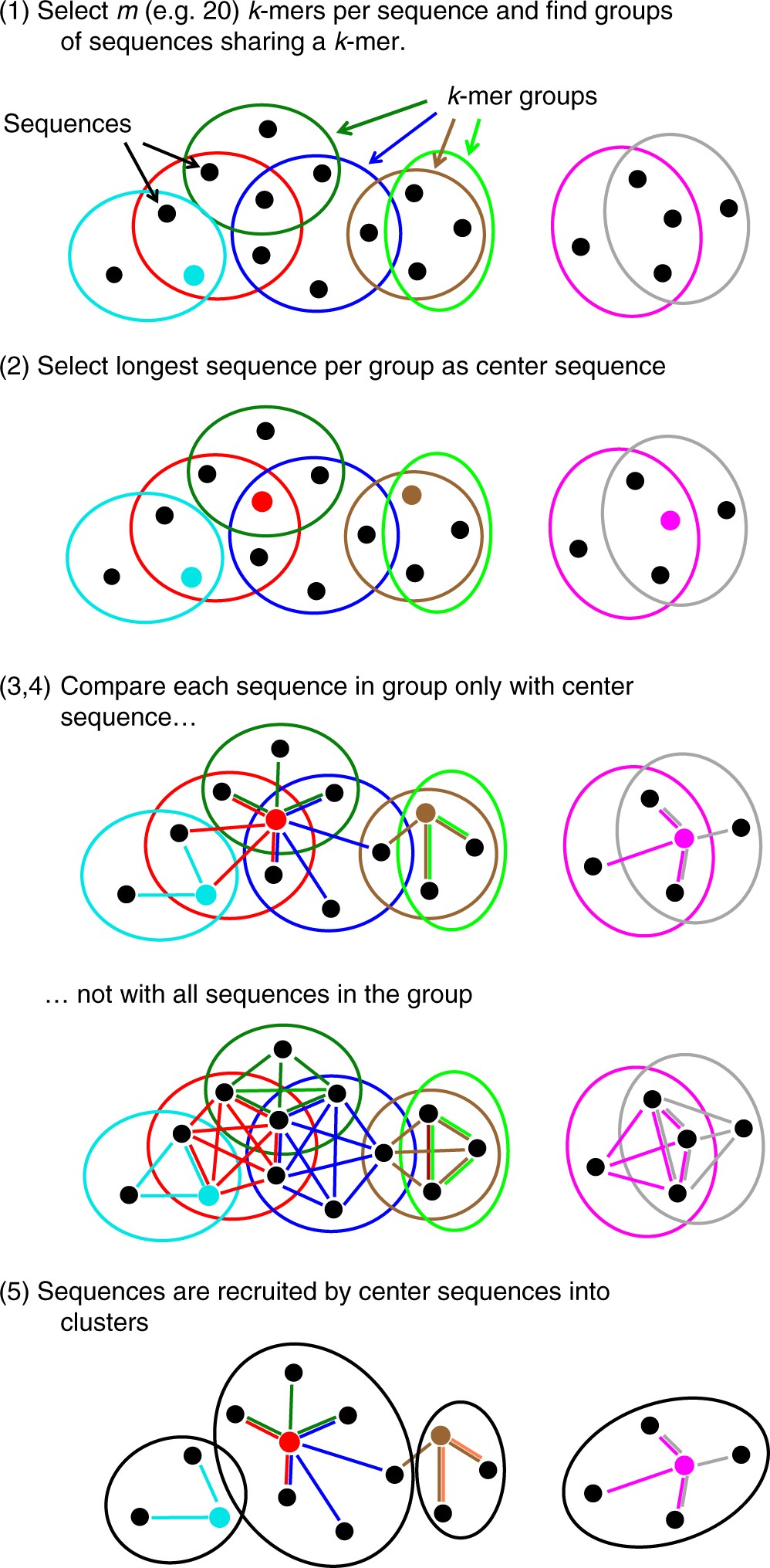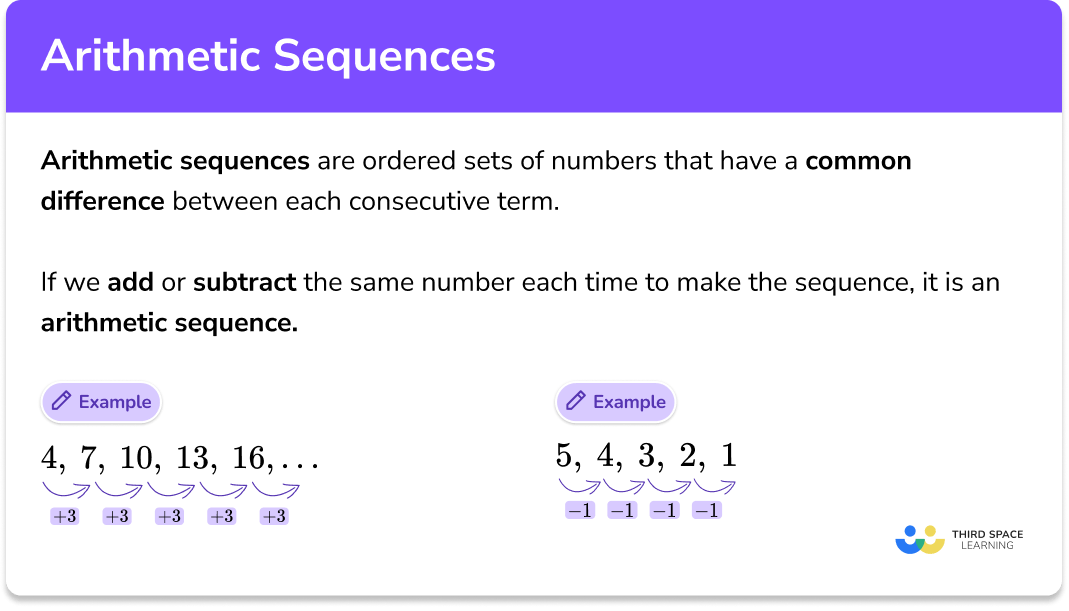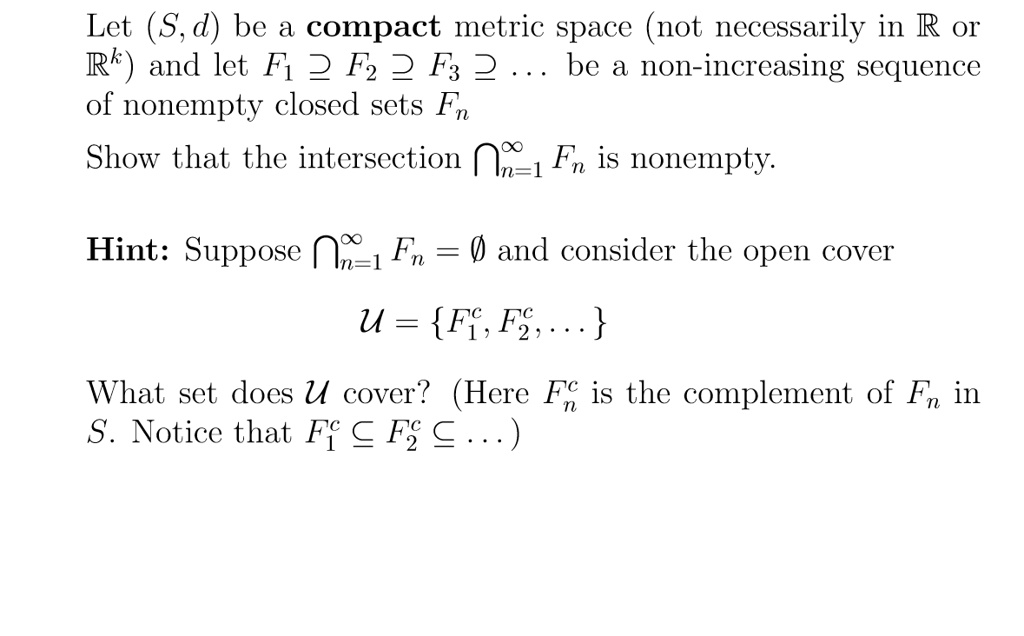
SOLVED: Let (S,d) be a compact metric space (not necessarily in R 0 Rk and let Fi 2 F2 2 F3 2 be a non-increasing sequence of nonempty closed sets Fn Show
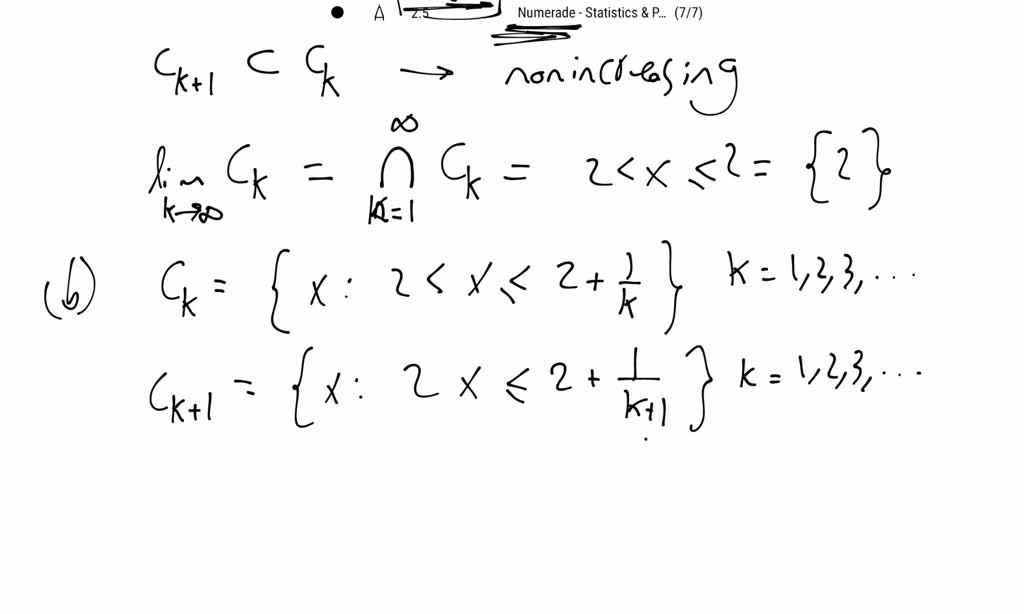
SOLVED:Show that the following sequences of sets, {Ck}, are nonincreasing, (1.2 .17), then find limk →∞ Ck. (a) Ck={x: 2-1 / k<x ≤2}, k=1,2,3, …(b) Ck={x: 2<x ≤2+1 / k}, k=1,2,3, …(c)

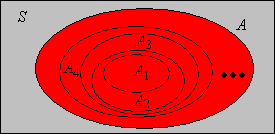
SOLVED: Let X be a set. A collection Ω of subsets of X is a monotone class on X if it is closed under monotone limits, in the sense that if An
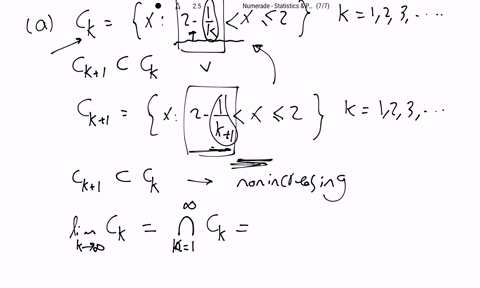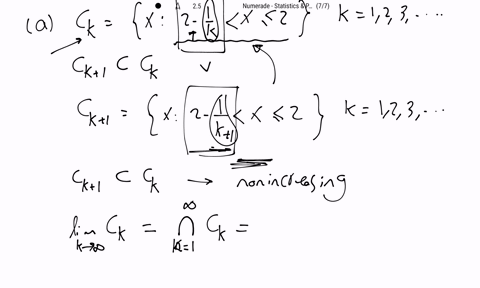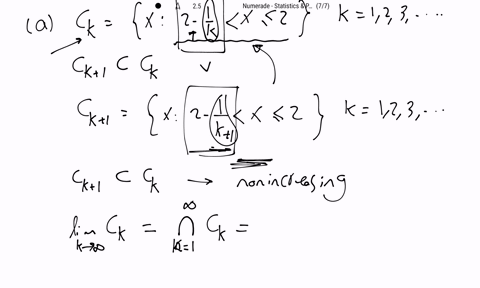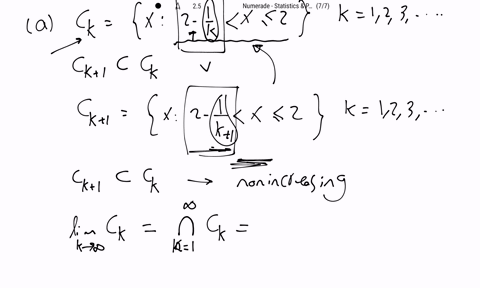
SOLVED:Show that the following sequences of sets, {Ck}, are nonincreasing, (1.2 .17), then find limk →∞ Ck. (a) Ck={x: 2-1 / k<x ≤2}, k=1,2,3, …(b) Ck={x: 2<x ≤2+1 / k}, k=1,2,3, …(c)

SOLVED: Let A = 2/n - 3/mn | n ∈ N. Show that A is bounded and find sup A and inf A. Does the set A have a minimum or maximum?
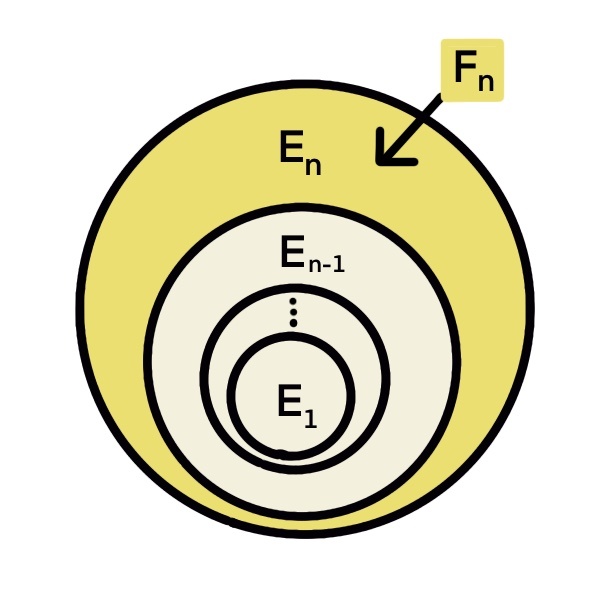
Interchangeability of Limits and Probability of Increasing or Decreasing Sequence of Events | Problems in Mathematics

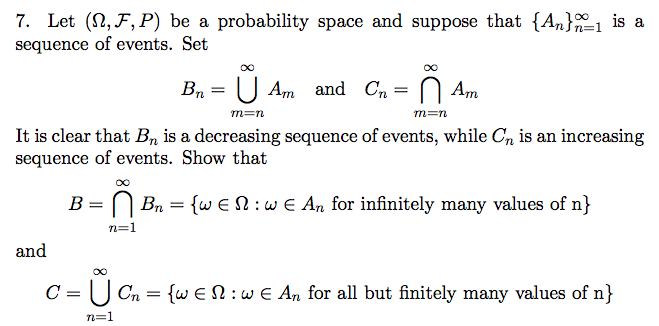
SOLVED: Title: Properties of Increasing and Decreasing Sequences of Events and their Applications in Probability Theory Fact: For any sequence of pairwise disjoint events Cn, we have P(U Cn) = Σ P(Cn)

Lecture 5: Computing the Measure of the Arbitrary Union/Intersection of Sequences of Measurable sets - YouTube